***Continued from Chapter 01 (Covered previously: Decision Intelligence and its meaning, The OODA Loop, How The OODA Loop Works: The Four Steps, Success Of The OODA Loop)
Link to Chapter 01:
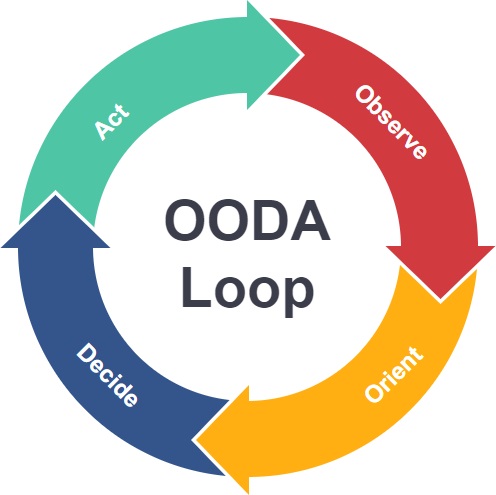
Uses Of The OODA Loop
In general, military planning models are often applied to uses outside of their original context due to their effectiveness in extreme situations. The OODA loop has been adapted to become an important concept in various fields such as business, game theory, information security, law enforcement, litigation, marketing and strategy. Professionals find this compelling because of its common-sense approach to decision-making and its emphasis on staying competitive.
With technology being used everywhere and more emphasis being placed on a company’s ability to collect feedback and analyze competition, this method is now a common approach applied in organizations. In business, OODA loops typically examine what is happening externally and how results are performing to become more agile. Similarly, an organization with a security operations centre (SOC), computer emergency readiness team (CERT) or computer security incident response team (CSIRT) may use an OODA loop cycle to develop an organization’s incident response plan.
Additionally, due to the growth of data analytics in business, the OODA loop is a popular method for handling an influx of constantly emerging information. Companies can achieve better situational awareness when they implement the observe and orient steps to organize data in a way that accurately depicts the business environment. Once the data is placed in context, they can make smarter organizational decisions and actions.
Examples Of The OODA Loop
In its simplest form, the OODA loop is employed by all individuals every day when making a decision.
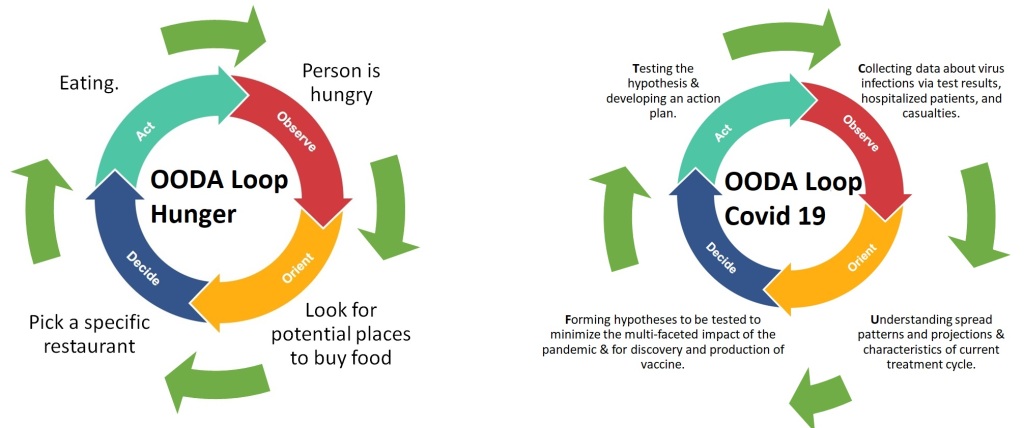
More complex, higher-stakes versions of the OODA loop in everyday life can be seen when creating a retirement savings plan or buying a home.

Alternatives To The OODA Loop
A few ideas that can be combined with the OODA loop include:
Plan, do, check, act (PDCA) cycle- This is a model geared towards continuous improvement that is also broken into four parts. The process starts by identifying a problem and gathering relevant data to the cause of the problem. Then, this information is used to develop and implement a solution. The results are then confirmed, or checked, before documented and used to make recommendations for further PDCA cycles.
Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats (SWOT) analysis– This is a framework used in business to identify and analyze any internal or external factors that could affect the success of a project.
Getting things done (GTD) method– This is a time management model that helps organizations break larger projects into smaller, actionable tasks. The GTD method is a five step process that is also sometimes referred to by the steps: collect, process, organize, plan and do. All material should be gathered, analyzed and categorized before being transforming into an action plan that is then carried out.
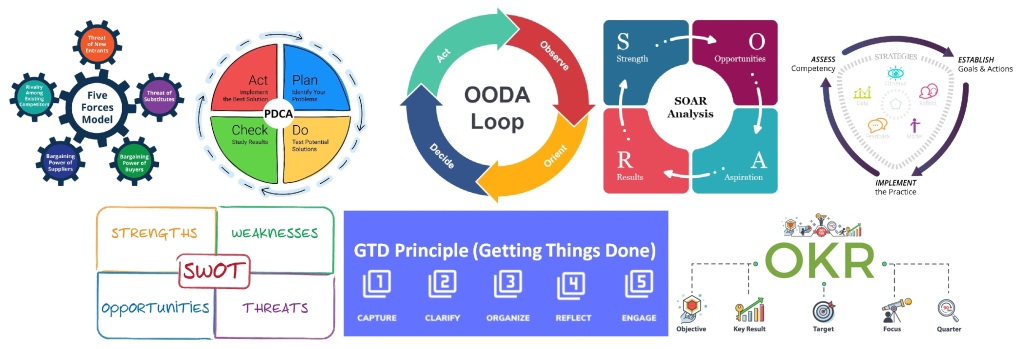
Objectives and Key Results– OKRs are frequently set and evaluated continuously during the project lifecycle to make sure everything gets done on time. They also act as future references to monitor how well you executed your projects.
Porter’s Five Forces– Porter’s Five Forces is a model that identifies and analyzes five competitive forces that shape every industry and helps determine an industry’s weaknesses and strengths. Five Forces analysis is frequently used to identify an industry’s structure to determine corporate strategy and in decision making.
SOAR Analysis– This is a framework for identifying Strengths, Opportunities, Aspirations and Results. It works in any business involved in any marketplace. Unlike some other frameworks, SOAR marries up fact finding about the company and position, alongside the desires of the stakeholders to aid better decision intelligence.
Decision Intelligence and Technology
During the recent decade, we saw a proliferation of data lake or data hub technologies. In spite of substantial innovations in dealing with three V’s of big data (Volume, Variety, and Velocity), we have yet to see any noticeable impact on the decision-action capability of organizations.
That does not imply that handling and managing data is unimportant for decision intelligence, however, we can safely conclude that it need not be the first step and some crucial piece is missing in crafting a decision intelligence system. A well-designed decision intelligence system is less dependent on data as one might think, as it can help make effective decisions even with limited data and can tolerate errors and inconsistencies as well as deal with high degrees of uncertainty.
Decision making being a cognitive function, we need a deeper understanding of it, so that we can better augment and support it by intelligent automation. Without this, it will be impossible to build an effective decision intelligence system. A decision intelligence system must be built around a sound decision making framework. Human and artificial agents can then collaborate following the structure and discipline of the framework.
The purpose and scope of decision intelligence automation is to implement artificial intelligence agents operating by the directives of a decision making framework. The least a framework does is to provide a structure and discipline without which an organization is bound to stay at the lowest level of decision intelligence maturity.
Decision Intelligence Frameworks Today
Early frameworks assumed that decision-making occurs at conscious level of processing guided by rational behavior. Today’s understanding of decision-making theories is much more nuanced:-
The SEAL Decision Model- Evolved specifically for designing human-machine collaborative decision intelligence systems, this stands for sense, explore, act, and learn. Though still transformational in nature, SEAL is designed to support and augment fundamental cognitive processes of human decision making rather than imposing on people to learn unfamiliar paradigms.
On first glance, SEAL may appear similar to OODA, since four elements of OODA can be loosely mapped to elements of SEAL as follows:
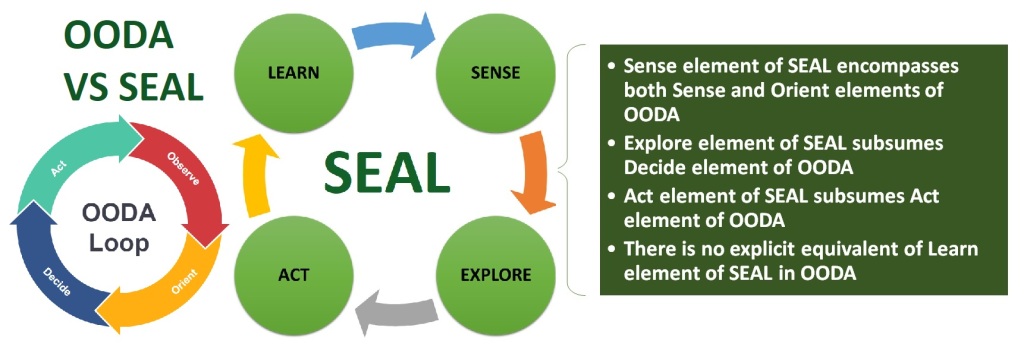
Human-Machine Collaboration In Decision Intelligence
The details under these elements are different because of the intent of SEAL to achieve a man machine symbiosis by reducing cognitive burden of decision makers and due to its continuous business optimization focus by explicit incorporation of feedback loops and learning. Some of these differences are:

Unlike Observe in OODA which is focused on sensing the current situation with the reactive intent, Sense in SEAL is proactive by design and predicts future situations that qualify as opportunities early so that organizations have ample time to become ready to react.
Sense agents may reveal multiple opportunities from the same snapshot of observation, thereby, requiring branching of subsequent activity to address them concurrently. Sense in SEAL requires active collaboration among human and machine agents as neither of them on their own can handle massive amount of data and make sense out of it.

Selected alternatives (similar to OODA hypotheses) move to the Action phase where actions are actually executed either manually or via a process automation substrate.
Learning happens at multiple levels – for adaption and fine tuning of predictive models and man-machine interaction. At a macro level, it is about understanding and improving the efficacy of action alternatives executed during ACT phase.
In summary, while OODA and SEAL are similar in emphasizing that a disciplined and facts based approach to decision making is essential for sustainable success in any endeavor, SEAL provides a comprehensive framework for implementing a human-machine decision intelligence system.

Content Curated By: Dr Shoury Kuttappa