***Continued from Chapter 01 (Covered previously: Decision Making, its styles, different Cognitive Biases)
Link to Chapter 01:
Common Patterns in Decision Making
The upside of understanding various patterns in decision-making is that they lead us to think about how the mind preforms its many complex functions in countless situations and how our awareness of time, space, and the various narrative and cognitive frameworks can help decode the factors that shape our decisions.
Here is a graphic presentation of what author Venkatesh Rao puts forward in his book. The graphic shows “Information Location” across the x-axis going from Internal to External and “Visibility of Mental Models” on the y-axis going from Low to High.
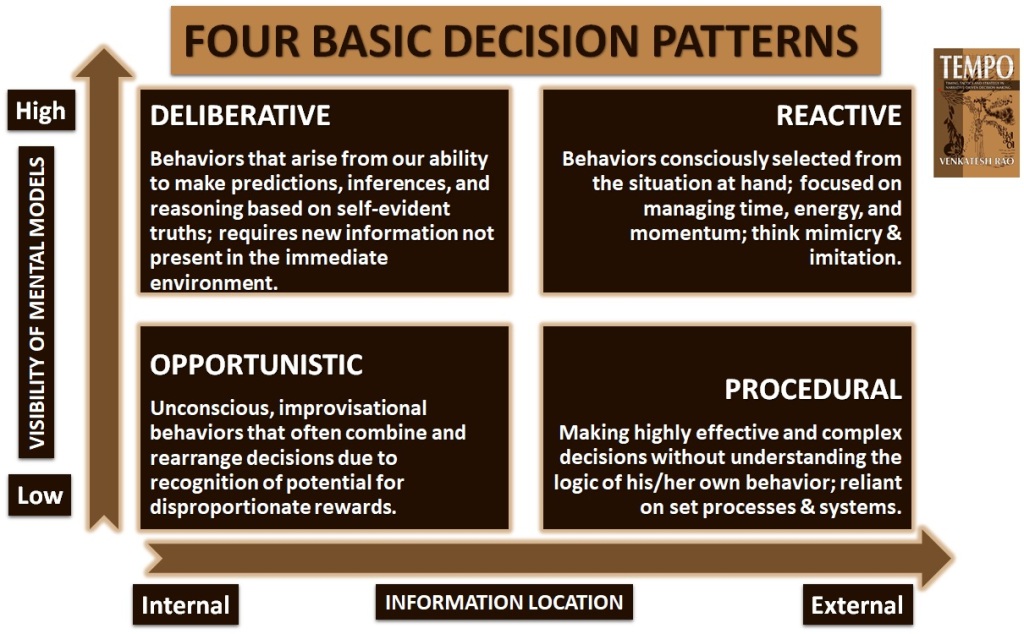
The distinctions among the four classes of basic decision patterns (above) are not arbitrary. They are based on the distribution and visibility of situational information. Information originates either in the decision-maker’s head or in the environment, and we either consciously recognize or are oblivious to the influence it has on our behaviour.
The ethical principles of decision making vary considerably. Some common choices of principles and the methods which seem to match them include:

Path dependency
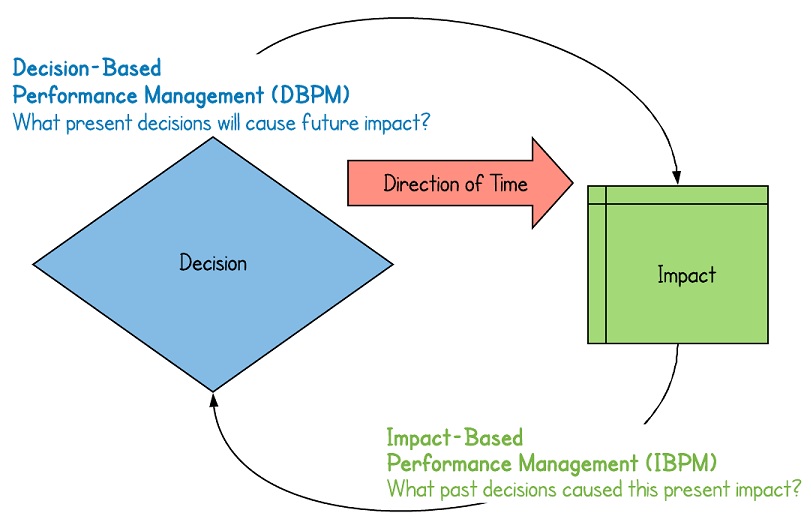
Path dependence is when the decisions presented to people are dependent on previous decisions or experiences made in the past. Path Dependence exists when the conditions for decision making is not based on current conditions, but rather has been formed by a sequence of past actions each leading to a distinct outcome. A common example is in Performance Management Systems.
Decision making in groups
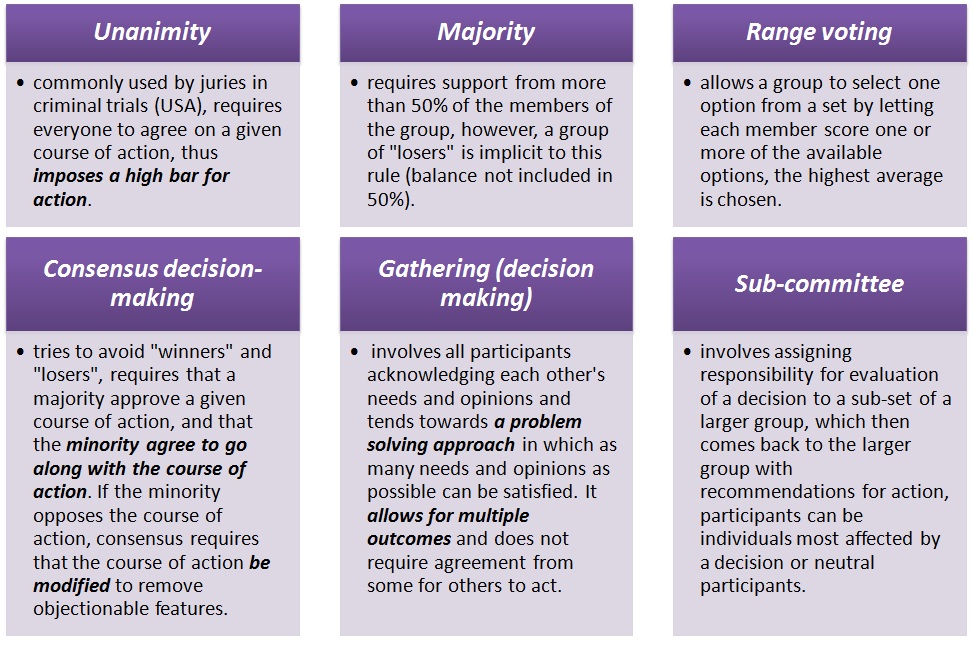
Decision making in groups is sometimes examined separately as process and outcome. Process refers to the group interactions. Some relevant ideas include coalitions among participants as well as influence, consensus and persuasion. In addition to the different processes involved in making decisions, group decision support systems (GDSS- protocol a group uses to choose among scenario planning alternatives) may have different decision rules, like:
Other less desirable group decision rules (group think) are:
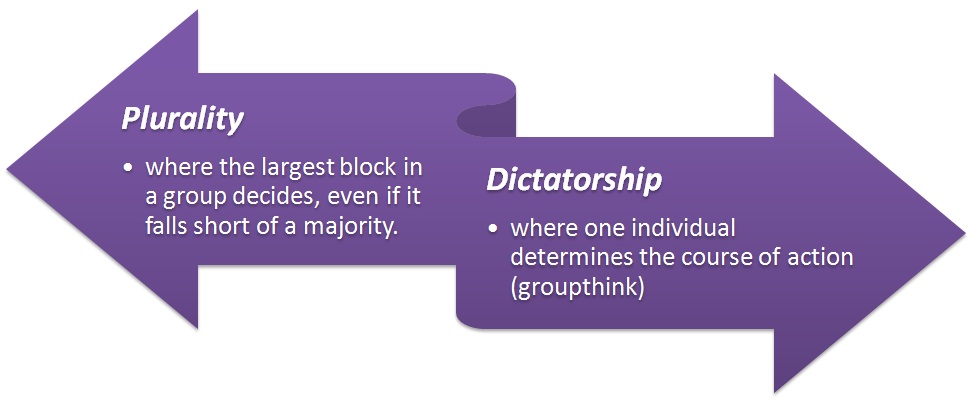
Plurality and dictatorship are less desirable as decision rules because they do not require the involvement of the broader group to determine a choice. Thus, they do not engender commitment to the course of action chosen. An absence of commitment from individuals in the group can be problematic during the implementation phase of a decision.
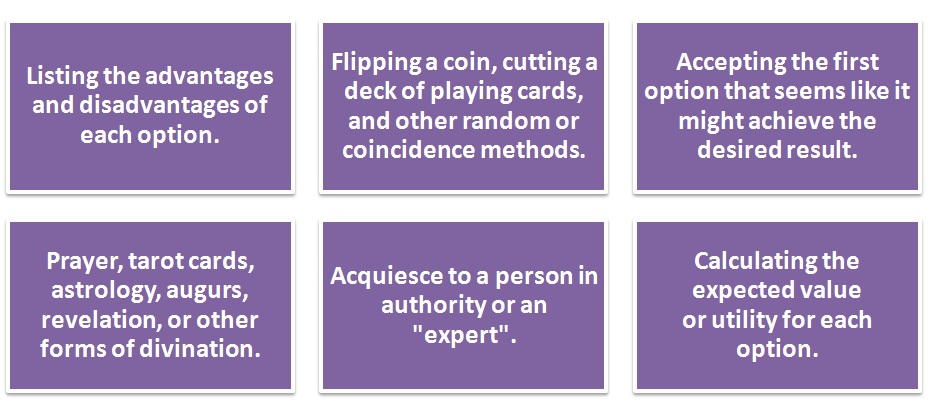
Decision making in one’s personal life
Some of the decision making techniques that we use in everyday life include:
Decision making in healthcare
In the health care field, the steps of making a decision are explained by the SHARE model:

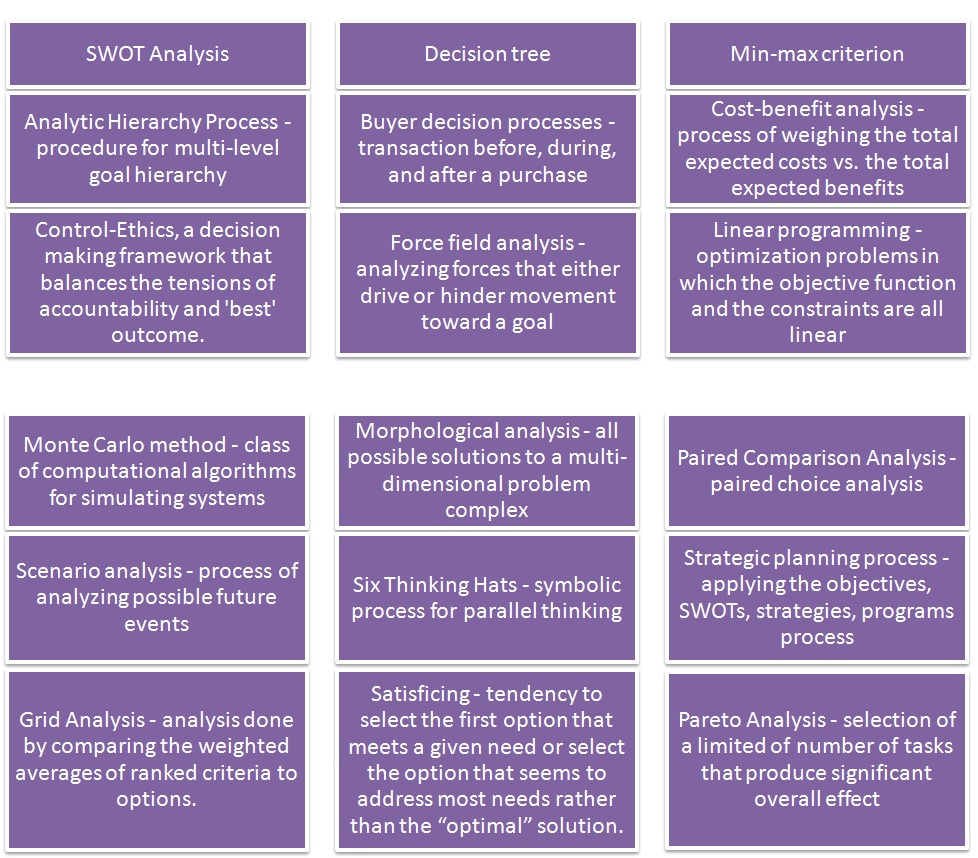
Decision making in business and management
Ideally, business and management systems may be set up to allow decision making at the lowest possible level. There is literature available on many models, some of which include:
Data-based business decision making may include the following cycle:
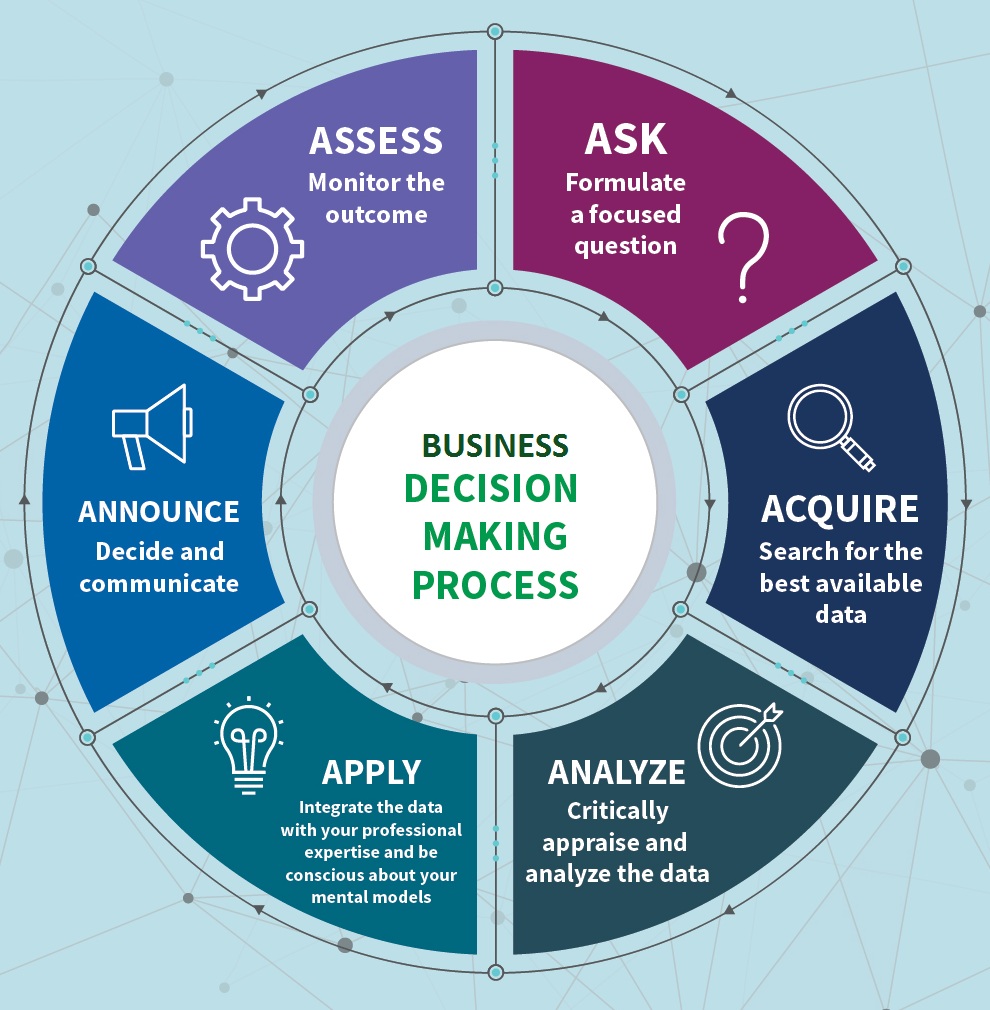
Caveat: There are no perfect decision making rules. Depending on how the rules are implemented in practice and the situation, all of these can lead to situations where either no decision is made or to situations where decisions made are inconsistent with one another over time.

Content Curated By: Dr Shoury Kuttappa.






