***Continued from Chapter 01 (Covered previously: Case Studies on Goals going Awry, Inappropriate Calibration of Goals, Impact of Time Horizon on Goals,)
Link to Chapter 01:
Goals Becoming Too Challenging
Proponents of goal setting claim that a positive linear relationship exists between the difficulty of a goal and employee performance. Specifically, they argue that goals should be set at the most challenging level possible to inspire effort, commitment, and performance—but not so challenging that employees see no point in trying. This logic makes intuitive sense, yet stretch goals also cause serious side-effects like:-
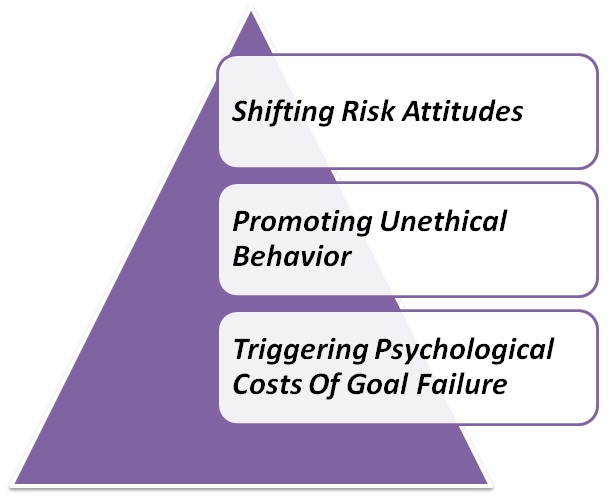
Shifting Risk Attitudes:-> Goal-setting often distorts risk preferences. People motivated by specific and challenging goals adopt riskier strategies and choose riskier gambles than do those with less challenging or vague goals. Related literature has found that goals harm negotiation performance by increasing risky behavior. Negotiators with goals are more likely to reach an inefficient impasse than are negotiators who lack goals. A negotiator who has obtained concessions sufficient to reach their goal, will satisfies and accept the agreement on the table, even if the value maximizing strategy would be to continue the negotiation process. Clearly, in some domains, goal setting can significantly harm performance rather than promote better outcomes.
In the 1996 Mt.Everest disaster in which eight climbers died due to the decisions of the two team leaders is an example of destructive goal pursuit. On Mt. Everest, world-class high-altitude guides, Rob Hall and Scott Fischer, identified so closely with the goal of reaching the summit that they made risky decisions that led to their own and 6 of their clients’ deaths. Some warning signs of leaders who have become excessively fixated on goals may be:
Unethical Behavior:-> Goal setting has been promoted as a powerful motivational tool, but substantial evidence demonstrates that in addition to motivating constructive effort, goal setting can induce unethical behavior. Goal setting can promote two different types of such behavior:
First, when motivated by a goal, people may choose to use unethical methods to reach it. For example, at Sears (reference – case study from chapter 01), mechanics told customers that they needed unnecessary repairs and then performed and charged them for this unneeded work.
Second, goal setting can motivate people to misrepresent their performance level—in other words, to report that they met a goal when in fact they fell short. For example, in 1993, employees at Bausch and Lomb who were driven to reach sales targets reported sales that never took place. They falsified financial statements to meet earnings goals.

Goal setting, of course, is not the only cause of employee unethical behavior, but it is certainly an important, understudied ingredient. A number of factors serve as catalysts in the relationship between goal setting and cheating: lax oversight, financial incentives for meeting performance targets, and organizational cultures with a weak commitment to ethics.
The interplay between organizational culture and goal setting is particularly important. An ethical organizational culture can reign in the harmful effects of goal setting, but at the same time, the use of goals can influence organizational culture. Specifically, the use of goal setting, like “management by objectives,” creates a focus on ends rather than means. Goal setting impedes ethical decision making by making it harder for employees to recognize ethical issues and easier for them to rationalize unethical behavior.
Psychological Costs of Goal Failure:-> One problem embedded in stretch goals is the possibility that the goal may not be reached. In negotiations, for example, challenging goals can increase negotiation and task performance, but decrease satisfaction with high-quality outcomes. These decreases in satisfaction influence how people view themselves and have important consequences for future behavior. It was found that giving someone a challenging goal versus an easy goal on an attention task or an intelligence test improved performance, but left people questioning their concentration abilities and overall intelligence. These goal-induced reductions in self-efficacy can be highly detrimental, because perceptions of self-efficacy are a key predictor of task engagement, commitment, and effort.
Fostering Collaboration and Learning in Goals
In order to adapt to a competitive landscape, organizations need employees who are able to learn and collaborate with their colleagues. Goals can inhibit both learning and cooperation.
Goals inhibit learning :-> When individuals face a complex task, specific and challenging goals may inhibit learning from experience and degrade performance. A person who is narrowly focused on a performance goal, will be less likely to try alternative methods that could help her learn how to perform a task. The narrow focus of specific goals can inspire performance but prevent learning.
“Learning goals” can be used in complex situations rather than “performance goals.” In practice, however, managers may have trouble determining when a task is complex enough to warrant a learning, rather than a performance goal. In many changing business environments, perhaps learning goals should be the norm. Even when tasks are complex enough to clearly warrant learning goals, managers face the challenge of identifying the specific, challenging goal levels for learning objectives.
Goals create a culture of competition :-> Organizations that rely heavily on goal setting may erode the foundation of cooperation that holds groups together. An exclusive focus on profit maximization can harm altruistic and other behavioral motives. Similarly, being too focused on achieving a specific goal may decrease extra-role behavior, such as helping coworkers. Goals may promote competition rather than cooperation and ultimately lower overall performance.

When Goals Harm Motivation Itself:-> As goal setting increases extrinsic motivation, it can harm intrinsic motivation – engaging in a task for its own sake. This problem is important, because managers are likely to over-value and over-use goals. Although people recognize the importance of intrinsic rewards in motivating themselves, people exaggerate the importance of extrinsic rewards in motivating others. In short, managers may think that others need to be motivated by specific and challenging goals far more often than they actually do. By setting goals, managers may create a hedonic treadmill in which employees are motivated by external means (goals, rewards, etc.) and not by the intrinsic value of the job itself.
Implementation and Calibration of Goals
Proponents of goal setting have long championed the simplicity of its implementation and the efficiency of its effects. In practice, however, setting goals is a challenging process, especially in novel settings.
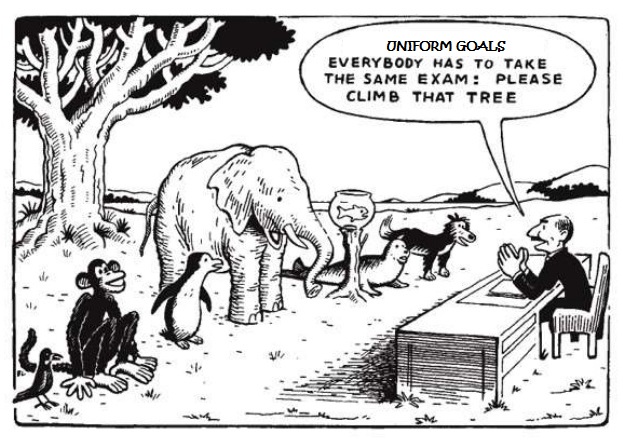
Goal setting can become problematic when the same goal is applied to many different people. Given the variability of performance on any given task, any standard goal set for a group of people will vary in difficulty for individual members; thus, the goal will simultaneously be too easy for some and too difficult for others. Conversely, idiosyncratically tailoring goals to each person can lead to charges of unfairness. This has important implications, because employee perceptions of whether rewards fairly match effort and performance can be one of the best predictors of commitment and motivation.
When reaching pre-set goals matters more than absolute performance, self-interested individuals can strategically set (or guide their managers to set) easy-to-meet goals. By lowering the bar, they procure valuable rewards and accolades. Many company executives often choose to manage expectations rather than maximize earnings. In some cases, managers set a combination of goals that, in aggregate, appears rational, but is in fact not constructive. In reality, CEOs (and many Wall Street executives) face asymmetric rewards—a large bonus for meeting the goal in one year, but no fear of having to return a large bonus the following year for underperforming.
Harnessing the Power of Goals
Goals can inspire employees and improve performance as well. Just as doctors prescribe drugs selectively, mindful of interactions and adverse reactions, so too should managers carefully prescribe goals. To do so, managers must consider—and scholars must study—the complex interplay between goal setting and organizational contexts, as well as the need for safeguards and monitoring.
According to General Electric’s Steve Kerr, an expert in reward and measurement systems, “most organizations don’t have a clue how to manage ‘stretch goals’”. He advises managers to avoid setting goals that increase employee stress, to refrain from punishing failure, and to provide the tools people need to meet ambitious goals.
It’s one thing to know about goal setting, and how it can help us, but another entirely to know how to actually set goals and stick with them. Goal setting tools are a great way to help us set goals, keep track of, and stay focused on what we are trying to achieve. These tools can be informal, for instance:
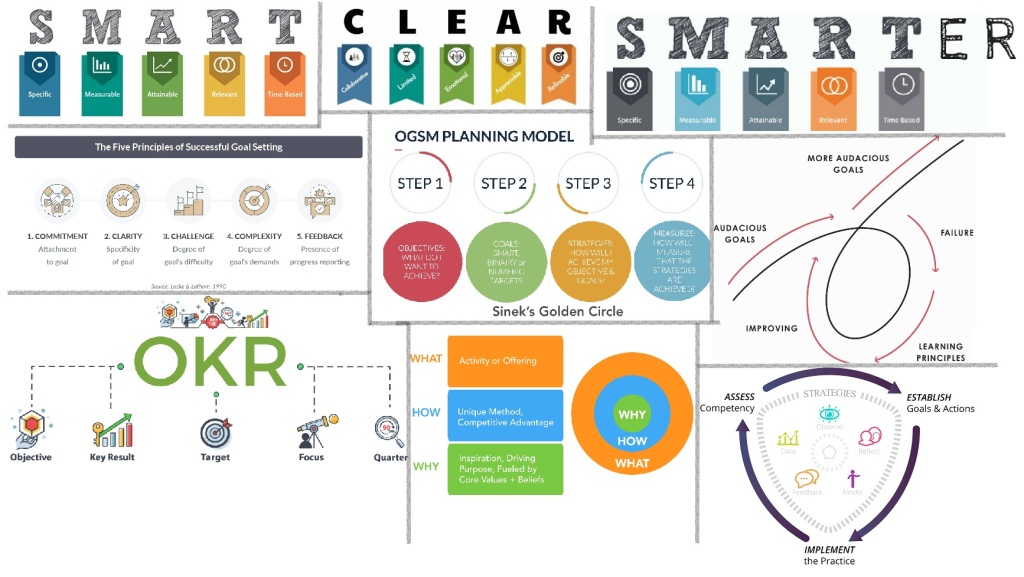
There are several concepts and tools for Goal Setting. Which tool is right for us will depend on what our goals are, how long we want to take to achieve them, and whether it is an individual or group goal.
Here are some popular tools:

Content Curated By: Dr Shoury Kuttappa.