We tend to think that we are who we are and there is not much we can do about that. But the fact is, we choose our personality and who we are. Our personality is shaped by the choices we make over time. One of the most frequent questions in personal development probably is “Can I change my personality type?” According to most personality type theories, the person’s type is inborn and does not change. However, people can develop traits and habits that differ or even directly contradict the description of their type.
An example may help us understand better. Suppose lights in the room suddenly go off and we are in complete darkness. We may be able to navigate our way to the door, but which of our senses will come into play? Touch? Hearing? Smell? It would be anything but vision, our preferred sense. As soon as the lights come back on, we will switch back to using vision again as it makes it much easier to navigate around the room.
The way our personality works is quite identical. The environment we are in shapes our personality in a certain way, forcing us to develop traits and habits that might be foreign to our type. For instance, if we are naturally casual and spontaneous, but our work schedule is very structured and our manager is obsessive about schedules, our preferences are likely to change. However, we will probably switch back as soon as we leave that job. The same rule applies to other traits as well.
Here it is important to consider that sociability is often confused with extraversion, just like shyness is confused with introversion – this is a common oversight when it comes to deliberating personality types. While extraverted people naturally find it easier to talk to other people (they gain energy when they do this), there are many shy or solitary people among them. Conversely, introverted types lose energy when they communicate with others, but you would be able to find many eloquent individuals in that group.
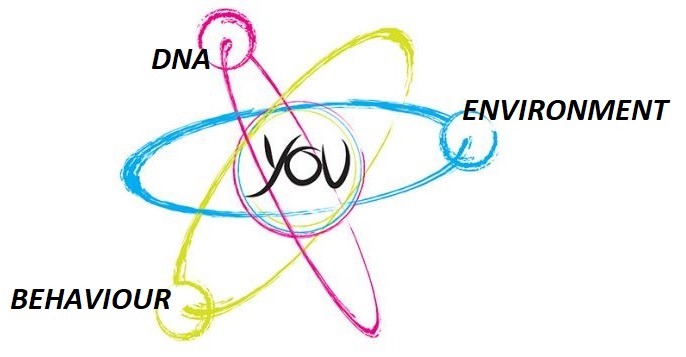
Does personality stay the same from birth for the rest of your life, or can it be changed? For decades personality was considered as unmalleable as concrete – who we were at age 15 is who we would be at age 75. But within the last 20 or so years, as cognitive and behavioural sciences have evolved, we have come to see personality as at least marginally changeable, and possibly much more so. While certain personality elements remain stable over time, others change in distinct ways. In other words, personality is both relatively stable and changeable, and the degree of change is specific to each person. As to what influences personality stability or malleability, both genetics and environmental factors play lead roles.
The relatively new wrinkle in this understanding is epigenetic influence, in which genes for certain factors may be “switched on” by environmental influences. What this means is that when it comes to personality change, we should not compare ourselves to others. Our especially likable and gregarious friend in middle school is still probably going to be more likable and gregarious than most people we know in mid-life. What matters is how much we have changed – and that is very much a person-specific evaluation.
Personality tests can be part of the problem. They are like a frame in a movie—just a part of the story of our life. They tell us where we are and, in that way, they are very valuable. Personality tests are self-reported. Our view of ourselves is constantly changing based on our current focus, context, and emotions.
Another aspect to consider is that anyone who has ever done something great with their life has had to transform themselves from who they are to who they became. They had to act accordingly beyond their current personality and circumstances to eventually do what they did and become who they became.
In this aspect, some fallacies (untruths) that limit our growth and potential are:
Fallacy #1: Personality Can Be Categorized into “Types”.
This states that the way we react to life is just “who we are,” and we should accept it, and not try to change it, and we could not if we tried. Even if those traits are limitations, there is nothing we can do about it.
There are no personality types that lock us into a way of being. These labels we take on tend to excuse us from taking personal responsibility for the behavioral outcomes we experience. We can shape our personalities to serve our goals. Our personality should come from our goals. Our goals should not come from our personality.
Fallacy #2: Personality Is Innate and Fixed
Our personalities change over time. Who do we want to be in the future is more important than who you are now, and should actually inform who we are now. Our intended future self can direct our current identity and personality far more than our former self can. We can use our future self as the filter for developing our personality in the present. Our future self can be evolved and different from our current self. Successful people start with a vision of their future self and use it as the filter for everything they do.
Fallacy #3: Personality Comes from Our Past
The idea that we are defined by our past or that the past is the best predictor of our future is true, but not because we cannot change. We simply have not for another reason.
Four reasons that keep people stuck in their past may be:

Past events can inform and change our present and future because we are learning from them. If not, we short-change our future. How we describe, interpret, and identify with our past has far more to do with where we are, here and now, than it has to do with our actual past.
Fallacy #4: Personality Must Be Discovered
Our personality, like our passion, is created by us and not discovered. It is designed. It is a by-product of the decisions we make. What we fail to understand sometimes is that inspiration follows action, not the other way around. Unless and until we take action, our confidence and imagination will remain low. We need to decide what we want and begin moving forward. With progress—even minuscule progress—our clarity and confidence will increase, opening the door for greater flexibility and change.
Fallacy #5: Personality Is Our True and “Authentic” Self
Our “authentic self” is a moving target, especially if we are of the kind to explore possibilities and are growing. To define ourselves with a fixed, authentic self is self-limiting and rigid. It lacks imagination and a growth mindset. Our authentic self is what we most believe in and who we aspire to be. Moreover, our authentic self is going to change. Being authentic is about being honest, and being honest is about facing the truth, not justifying our limitations.

The Gap and the Gain
When we are in the gap, we cannot enjoy or comprehend the benefits in our life. All we are focused on is why something was not how we thought it should have been. For instance, we might live in a great house. But if we are in the gap, then all we might see is what is wrong with our house. We may have an amazing partner but only see what we believe to be wrong or missing in them.
As we get older, we tend not to put ourselves into new contexts, so our personality becomes predictable. We get into our comfort zones. We see consistency in everyday life because of the power of the situation. Putting ourselves in new environments, around new people, and taking on new roles is one of the quickest ways to change our personality, for better or worse.
To conclude, our basic personality type cannot change – however, we can change the aspects of your personality that we are unhappy with. By doing this we will strengthen our shadow traits and become a more well-rounded individual, even though our dominant traits will still remain the same. Such a change could be triggered by either the environment we are in or our own will – to each his own.
**Source Credits: Parts adapted from The Book:- Personality Isn’t Permanent By Benjamin Hardy
Content Curated By: Dr Shoury Kuttappa.