***Continued from Chapter 01 (Covered previously: What Is Big Picture Thinking, Importance Of Big Picture Thinking, Detail Oriented Or A Big Picture Thinker- The Difference)
Link to Chapter 01:
Identifying the Different Approaches – Approach Indicators
No matter which field we belong to – an aspiring entrepreneur, someone who’s putting together a dream team, or polishing our leadership skills, big picture thinking can help open up, innovative and unexpected creative paths, ideas and solutions.
Detail-Oriented Approach Indicators
- We prefer tweaking an existing plan than creating one from scratch
- We think over issues in such great detail that we sometimes miss the bigger picture
- We end up putting down or highlighting almost all notes
- We work towards high-quality work in most areas of our life and struggle with perfectionist tendencies
- We’re organized and/or like routine
Big Picture Approach Indicators
- We can easily spot patterns in problems
- We have a low tolerance for busywork, tedious errands, and routine
- We are good at figuring out an overview of strategies to get something done
- We get bored when we have to deal with the tiny details of a project
- People view us as incredibly creative and we like to come up with original ideas
- We don’t obsess over little details and therefore, solve problems fairly quickly
The Balance: Big Picture & Detailed Orientation- Components in Business
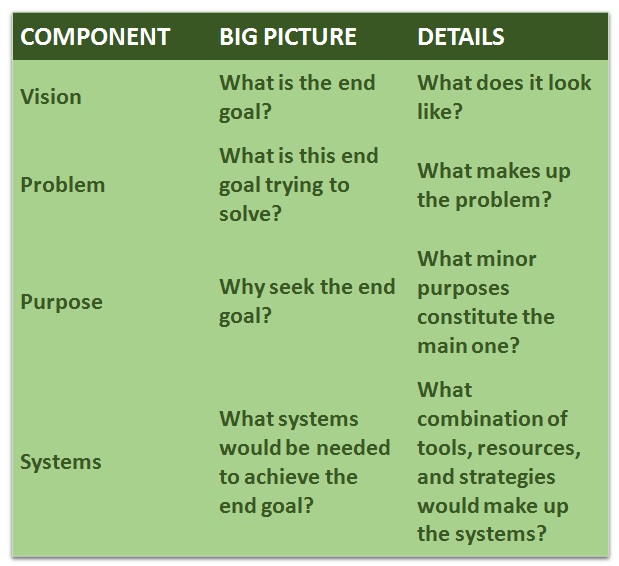
Strategies Towards a Big Picture Focus
A) Identify habits that limit our big picture thinking ability:. . . Our natural preferences often prevent us from blue sky thinking. So, the first step: break bad habits. Here’s a 3-step framework:

B) See things from a different lens: . . . Diving into big picture questions helps us connect the dots from our actions/tasks to the big goal. In this book, The Magic of Thinking Big, David J. Schwartz calls this, “see what can be, not just what is.” A good starting point is to ask ourselves, ‘what am I trying to achieve?’ Some big picture questions may be:

C) Think big by looking up: . . . The super basic rundown is that whenever we are focusing on the big picture, look up. And look down when not seeing the big picture.
A nice example of chunking reasoning is to think of transport. We can start with a motor car. If We chunk down, We might go to wheel, then rim, then rubber, then tread and even road. If We chunk up, We might go to transport, then to travel, then to vacation, then to wellbeing, etc.”
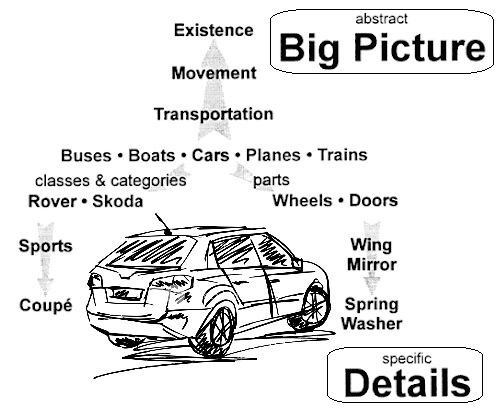
D) Use bulleted lists to think big: . . . This is a trick many of use on a regular basis – making a bulleted list of the big picture and then adding sub-bullets to each pillar step. We can then step back and look at what can be added or removed from the sub-bullet pointers to keep the needle moving forward.
So why did this work? Because bullet points give us the visuals on the big picture. It’s challenging to connect the dots when we can’t see them. It’s also tough to translate the big picture if we don’t have it in front of us. What’s more, bullet points are easy to access and revise anytime. This, in turn, provides clarity.

E) Start journaling / mind mapping: . . . When we put our internal prattle on paper, we can easily spot where we are flailing or how it can be shaped to fit the bigger picture. To begin with, note down the big picture, followed by the small details pestering us. The trick is to make sure that it represents not only the big picture, but that it represents the detail, or actionable elements as well. Then record our thoughts to see if they deviate from the big picture plan.
F) Schedule in some thinking time: . . . Often, when we rush to make a decision, we end up feeling sorry about it. When this happens, it’s usually for one of three reasons:
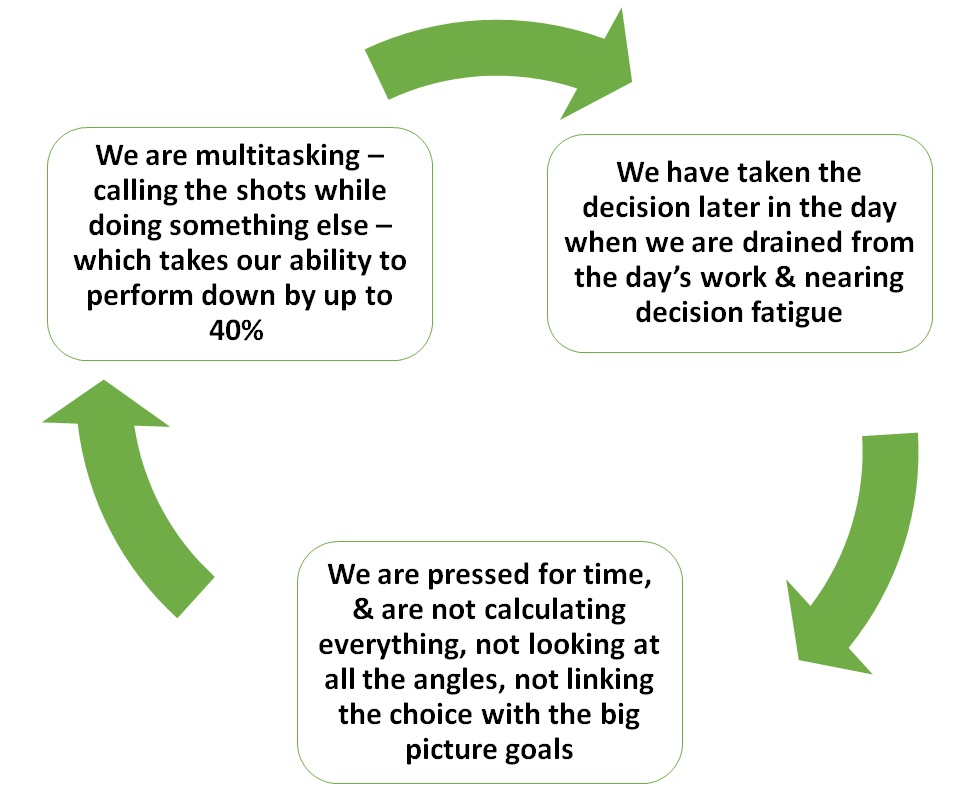
If we find ourselves nodding yes to any or all of these points, pencil in some uninterrupted, thinking time to our schedule. This space is crucial to making better decisions that rely on the big picture. We will also be able to rate our priorities better – what matters in the big picture, how it contributes to the big picture and so on. This will help us to stop hustling so hard, and ditch the shiny object syndrome.
Self Reflection- The Key
If we pause and contemplate how we are doing, we can make small tweaks that help us stay consistently productive. Some pointers to reflect on may be:
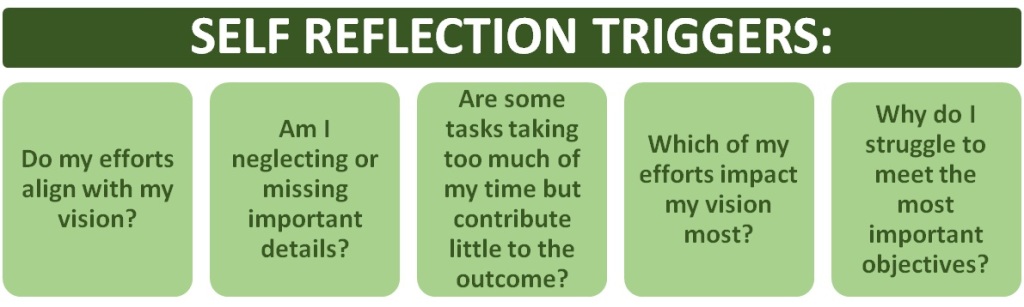
When we are busy executing any tasks in our lives for far too long, it’s easy to forget the details or the big picture depending on the type of thinker we are. For instance, as a big picture thinker, we may be excited by how our old and new ideas are connecting and work on outlining them, forgetting that the ideas have to be structured by many crucial details to work in the long term. The details person on the other hand might be buried in unending to-do-lists, feeling secure in the routines only to be disrupted by an enormous transition they didn’t anticipate.

Content Curated By: Dr Shoury Kuttappa