***Continued from Chapter 01 (Covered previously: Components of Authentic leadership, Characteristics Of Authentic Leaders, Significance of Authentic Leadership, Developing Authentic Leadership)
Link to Chapter 01:
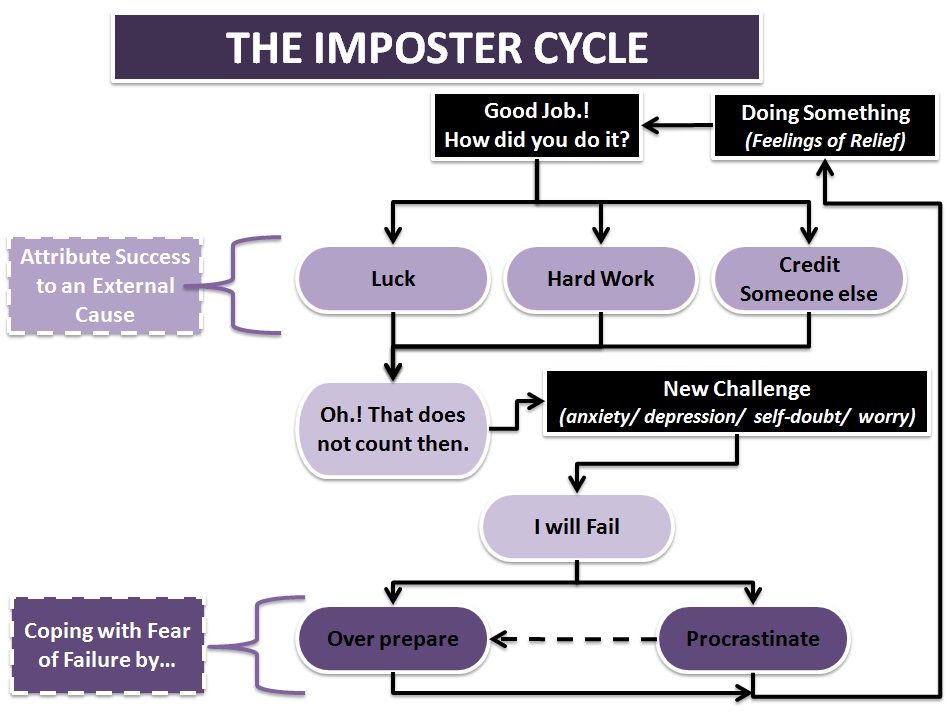
Transactional vs Authentic Leadership – The Difference
Transactional leadership is also called Managerial Leadership. It works in a structured system where authority and the chain of command are clearly demarcated. The philosophy works on the principle of transaction, i.e., give and take of reward and punishment. The leader uses the carrot and stick transactional leadership approach to get work done from subordinates. If we consider Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, Transactional Leaders can be said to address the lower-level needs of security and acceptance.

Transactional leaders aim to fulfil their subordinates’ needs of security and social belonging that are at the bottom of this pyramid. The higher-level needs of esteem and self-actualization remain unaddressed by such leaders. Transactional Leadership works within a set organizational culture, and does not attempt to change or transform the culture as Transformational Leadership does.
Managers following this transactional leadership model place a lot of value on profits and share value, and keep their eyes fixed on the bottom line. Monetary benefits matter a lot to managers of transactional leadership mentality, to the extent that these drive their actions and their relationships with subordinates.
Authentic Leadership follows ancient Greek philosophy focusing on developing prudence, temperance, justice and fortitude in a leader. Authentic leadership is based on the leader’s ethical and honest relationships with followers. Trust and openness are the hallmark of such leaders. As the name suggests, authentic leaders are genuine about their relationships and their transactions. Authentic leaders value personal relationships and ethical interactions over monetary authentic leadership benefits and profits. Naturally, workers trust such leaders and are enthusiastic about working for them. Team spirit and individual effectiveness flourish in such an atmosphere.
So, the principles of authentic leadership are basically those of openness, trust, and doing away with pretenses and deception. Authentic leadership does not involve play-acting, in which leaders exhibit a different personality in the workplace and a different one in their personal lives. Authentic leaders demonstrate these five qualities:
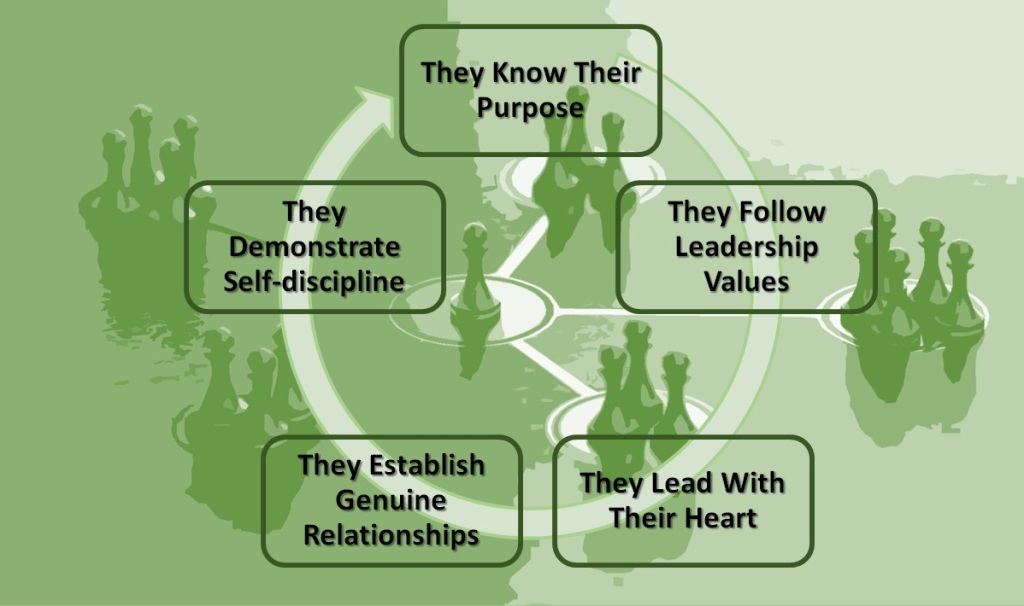
The authentic leader’s personal history, including life-events (trigger events), help in leadership formation. The moral development and values of authentic leaders are influenced by these personal histories and trigger events.
Transactional vs Authentic Leadership

Unearthing Our Authentic Leadership
How do we develop as an authentic leader? Discovering our authentic leadership requires us to test ourselves, our values, and our beliefs through real-world experiences. This is not an easy process as we are constantly buffeted by the demands of the external world, the model of success that others hold out for us, and our search to discover our truth. Because there is no map or direct path between where we are now and where we will go on our leadership journey, we need a compass to stay focused on our True North and get back on track when we are pulled off by external forces or are at risk of being derailed.
The compass is a dynamic tool that you can update and calibrate after every experience to ensure that each step we take on our leadership journey is consistent with how we want to lead our life. Because our circumstances, opportunities, and the world around us are always changing, we will never stop calibrating our compass.
When each part of our compass is well developed, we will be pointed toward our True North. The following fundamental questions can help in calibrating ourselves towards our true north:

Authentic Leadership and Emotional Intelligence
Self-awareness is the first element of Emotional Intelligence, or EQ, that psychologist Daniel Goleman, author of Emotional Intelligence, uses in describing the leader’s role. While intellectual intelligence, or IQ, has long been thought of as an essential characteristic for managers, EQ may be more important for authentic leaders. Too many leaders believe that by being the smartest person in the room, they can use their intellect to carry the day. As a result, they over-power less forceful voices that may have the vital ideas, insights, and answers they need to succeed.
- Finding the Right Role. . . – >
Whether we are in a start-up, a turnaround situation, or a growth opportunity, the better we know ourself, the more likely we are to choose the right role for ourselves.
2. Increasing Self-Confidence. . . – >
When leaders know themselves well, they become comfortable in their own skin. Adobe CEO Bruce Chizen once felt insecure about working in the technology industry because he was not an engineer. When he recognized his strong business and product-marketing skills and his ability to learn about engineering, a switch flipped in Chizen’s mind. After that, he became increasingly self-confident: “I understood myself well enough to know what I didn’t know, but also knew enough to feel comfortable. That awareness helped me find real self-confidence.”
3. Being Consistent. . . – >
By being aware of their actions and intentions, leaders act consistently in different situations and gain the trust of others. Former American Airlines CEO Don Carty reasoned, “You cannot motivate people unless you talk and walk in the same way. How can you expect an employee to be pleasant with a customer if you’re not pleasant with the employee?”
4. Connecting with Others. . . . – >
Most leaders see the process of gaining self-awareness as crucial to their ability to build strong relationships. Those who are comfortable with themselves tend to be more open and transparent—which includes sharing their vulnerabilities.
5. Complementary Skills. . . . – >
Leaders who know their strengths and weaknesses can fill their skill gaps with colleagues that complement them. Ned Barnholt, Agilent’s former CEO, said, “You understand your strengths and shortcomings and try to build a strong team around you. I didn’t grow up as an accountant so I surround myself with excellent financial people. That’s a lot better than trying to be somebody you’re not.”

The advice to “know yourself” is thousands of years old. But knowing ourselves at the deepest level is not easy, as we are complex human beings with many aspects to our character. We are constantly evolving, as we test ourselves in the world, are influenced by it, and adapt to our environment—all in an attempt to find our unique place.

Content Curated By: Dr Shoury Kuttappa