Being present with oneself, in the moment, being mindful, mentalizing, reflective function—all of these constructs point toward a crucial recognition of one’s own experience that takes place repeatedly on short time scales, as much as it is an overarching way of seeing that spans a lifetime. Practicing curiosity fosters open-mindedness.
There is a firm but gentle way to be intently aware, where one almost sees oneself as a beloved stranger. Being a stranger to oneself can represent alienation and nihilism, but it can also be the beginning of a love affair as we meet ourselves anew. Closeness to oneself, however, can pose a variety of real and imagined threats. It is important to respect our own boundaries, self-consent to all major decisions, and equip ourselves well.
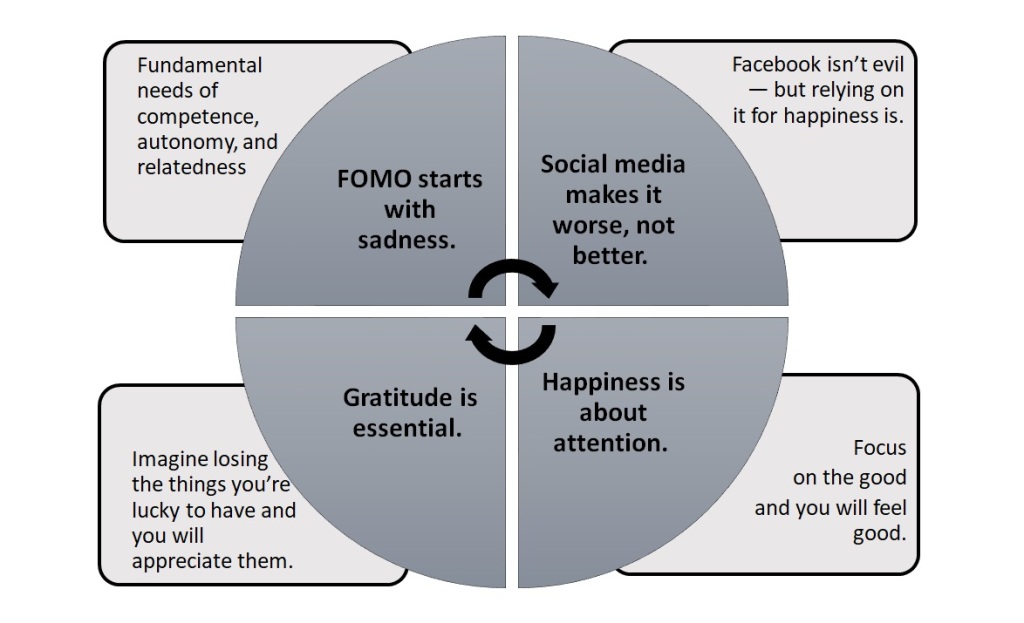
Self-Absorption vs. Self-Reflection
In the journey of self-discovery and personal growth, two seemingly similar yet fundamentally different concepts often arise: self-absorption and self-reflection. While both involve introspection and inward focus, understanding the nuances between them is crucial for fostering genuine growth and avoiding potential pitfalls.
The Key Distinctions: Intentions and Outcomes
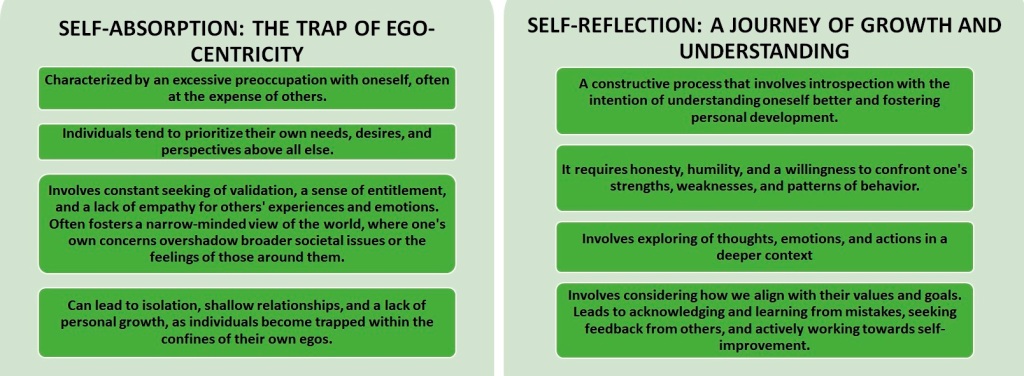
At the core of the distinction between self-absorption and self-reflection lie the intentions and outcomes of each mindset. Self-absorption is driven by a need for validation, self-aggrandizement, and the preservation of one’s ego. It often leads to stagnation, interpersonal conflicts, and a lack of meaningful connections.
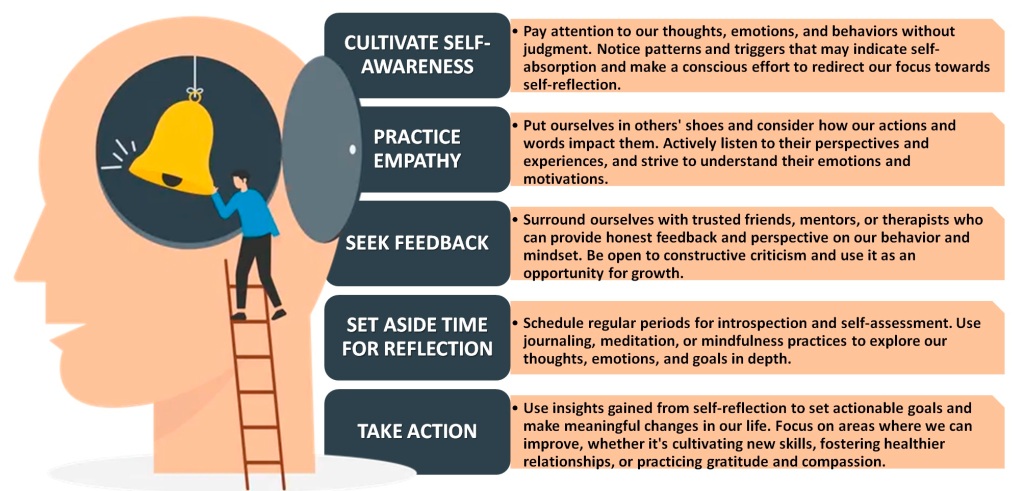
In contrast, self-reflection is motivated by a genuine desire for personal growth, understanding, and empathy. It fosters deeper connections with oneself and others, promotes self-awareness and emotional intelligence, and cultivates resilience in the face of challenges. Achieving a balance between self-absorption and self-reflection requires mindfulness and conscious effort. Here are some practical strategies to navigate this balance effectively:
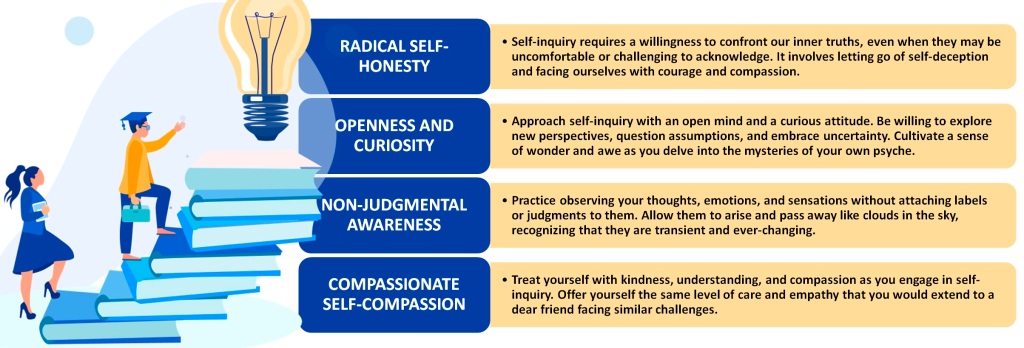
Understanding Self-Inquiry
Rooted in various philosophical and spiritual traditions, self-inquiry involves a deep exploration of one’s thoughts, emotions, beliefs, and motivations. At its core, self-inquiry is a process of asking ourselves profound questions and reflecting on the answers that arise. These questions may vary depending on individual needs and circumstances, but they often revolve around themes such as identity, purpose, values, fears, desires, and relationships. Through self-inquiry, we seek to unravel the layers of conditioning, assumptions, and unconscious patterns that shape our perceptions and behaviors. Key Principles of Self-Inquiry may include:
The Dangers of Excessive Self-Reflection: When Introspection Becomes a Trap
Self-reflection, like any tool, can be misused or taken to extremes, leading to a host of negative consequences.
- Paralysis by Analysis: The tendency to overanalyze every aspect of our thoughts, feelings, and actions. Instead of leading to clarity and understanding, this can result in a state of paralysis where individuals become stuck in endless loops of rumination and indecision. They may find themselves constantly second-guessing their choices, unable to take action for fear of making the wrong decision.
- Increased Stress and Anxiety: Constantly scrutinizing our thoughts and behaviors can also lead to heightened levels of stress and anxiety. When we are hyper-focused on our perceived flaws and shortcomings, we are more likely to experience negative emotions such as worry, self-doubt, and fear of failure.
- Self-Obsession and Narcissism: Excessive self-reflection can also fuel self-obsession and narcissistic tendencies. When individuals become overly fixated on themselves and their own needs, they may lose sight of the bigger picture and struggle to empathize with others. This can lead to a sense of entitlement, a lack of empathy, and difficulties in maintaining healthy relationships. Eventually it can result in feelings of loneliness, isolation, and a lack of meaningful connections.
- Inhibition of Spontaneity and Creativity: Constantly analyzing every thought and idea can stifle innovation and prevent individuals from taking risks or thinking outside the box.
- Distorted Self-Perception: Excessive self-reflection can also lead to a distorted self-perception, where individuals become overly critical or judgmental of themselves. They may magnify their flaws and shortcomings while minimizing their strengths and achievements. This can erode self-esteem and confidence over time, leading to feelings of inadequacy and unworthiness.
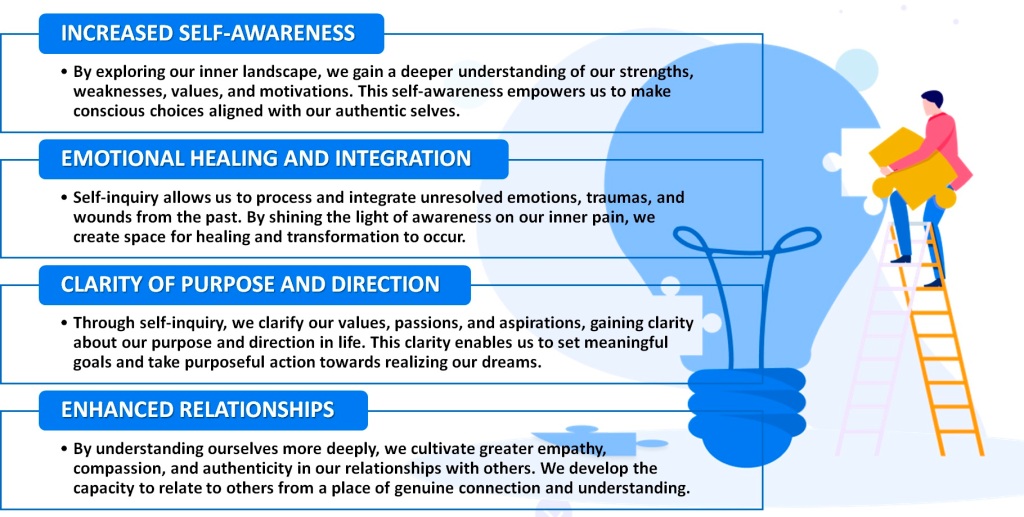
Benefits of Self-Inquiry
The practice of self-inquiry offers a multitude of benefits for personal growth and well-being:
Self-Inquiry Is A Complex Affair
There are so many layers and options, and fully cataloguing every dimension would be quite an undertaking. Taking it all in and using it implicitly would be ridiculous. In the meantime, here are a few questions and related observations, which may be handy.
A) Why am I thinking this? I mean this thought, right now: . . . While this can simply be a curious question, it may feel critical particularly if the emotional tone (the inner tone of voice) is short or explicitly berating. However, there is a possibility that this is a useful question, as it allows one to trace back the origins or triggers of a particular train of thought or sequence of experiences. “How come” or “when did you first notice this” can be other ways to wonder why.
B) What is happening? This is what is passing through my mind: . . . This feels like recognition, though the content may change. There is a sense of sureness, no doubt. It may be a fleeting notion, or an old familiar companion. Getting such repeating complexes of thought-emotion-behaviour, holistic experience, is useful. They may represent the brain’s resting state network, or default mode network (DMN) activity. Many people do not pay attention to this background noise, but it is not fully random. There are often large parts which are consistent over time. Whether they work as we wish, and so on, is another question.
C) What am I seeing? More to the point, where is attention focused?: . . . . A lot of how we think is in a visual mode. The mind is a high-entropy system, meaning it can be in many possible states. According to physicist Emerson M. Pugh (though often ascribed to others), “If the human brain were so simple that we could understand it, we would be so simple that we couldn’t.” We can imagine anything, given enough time, but the reality is that at any given moment we have a limited capacity to hold information in mind. This is the paradox of the brain, which is effectively infinite to itself while being severely constrained, as in theory I can think, say or experience a massive number of possible things. In the visual metaphor, we can control how far away we are from the object of attention, creating a degree of detachment without disengagement.
D) Am I listening? Did I stop listening to what is important to me?: . .. . Listening is key because we can expand the soundscape of how we take our own thoughts. Sometimes the littlest voices are the most important, as is often said. For example, suppose we look at it in different modes. Our default listening mode is meant to meander, and meandering is healthy, creative, and restorative. It lets us stumble upon interesting and potentially important things we might otherwise zip past. The executive control mode can remember what was prioritized, execute plans, and direct resources. The salience mode decides what to highlight and what to filter out, to a significant extent based on past experiences, for better or worse. Clearing the mind makes listening easier.
E) Am I using all my senses? . . . . Other ways of self-attention track with other sensory modalities, scent or olfaction, touch, taste, body sense or proprioception, and subtle cues of a very basic nature, such as level of tension and groundness, feeling uprooted or firmly planted. It takes a bit of a Sherlock Holmes mentality to fully get a sense of oneself first by looking for all the tell-tale clues. Any sense can be a metaphor or template for ways of inner perception. The immersion in digital reality tends to make it harder to cultivate other senses, though, as audio-visual systems get disproportionately used, and highly developed. Adaptations to cyber-reality may make it harder to be present in an embodied form, as we come to expect and have become accustomed to obvious simulation. It also changes the way we relate to one another.
F) Am I present? . . . . . The act of asking this question, which may be dispassionate and compassionate, can have the immediate effect of returning one to the present. This is especially true if the path is well-travelled. Neurotic tendencies interfere, with second-guessing and worry. It is like building a bridge into the air over a canyon without being able to see the other side. Being present uses up mental resources, taking other brain systems offline, such as those involved in excessive worry. It also means that we cannot think about the past and future in quite the same ways, as there is a sense of time standing still in the present moment. Long-term planning from this perspective is more of a blueprint, perhaps as imperfectly glimpsed in a dream.
There is a question of whether humanity has been sleepwalking — a manifestation of collective self-hypnotic somnambulism — and whether we are becoming woke, or not. Being present allows us to at least take stock of our personal inventory, possibly catching more of what we ordinarily downplay or completely miss.
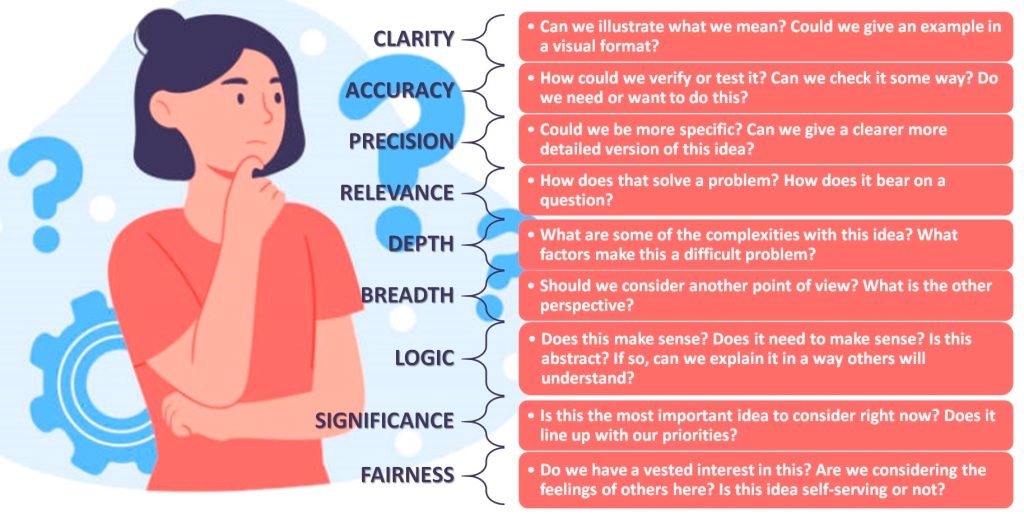
Sometimes we have an idea, and while we are thinking about it, we realize we are struggling to clarify to ourselves what we are really thinking. We have an idea and wanted to communicate it to someone else, but find ourselves saying, “it’s hard to explain”. Some questions that may help us out of this are:
Content Curated By: Dr Shoury Kuttappa